Neurological Disorders
The purpose of this website is to provide educational information for practitioners on biologic materials, orthopedic protocols, regulatory considerations, and general best practices. This content is intended for professional education only and does not constitute medical advice or approved treatment recommendations.
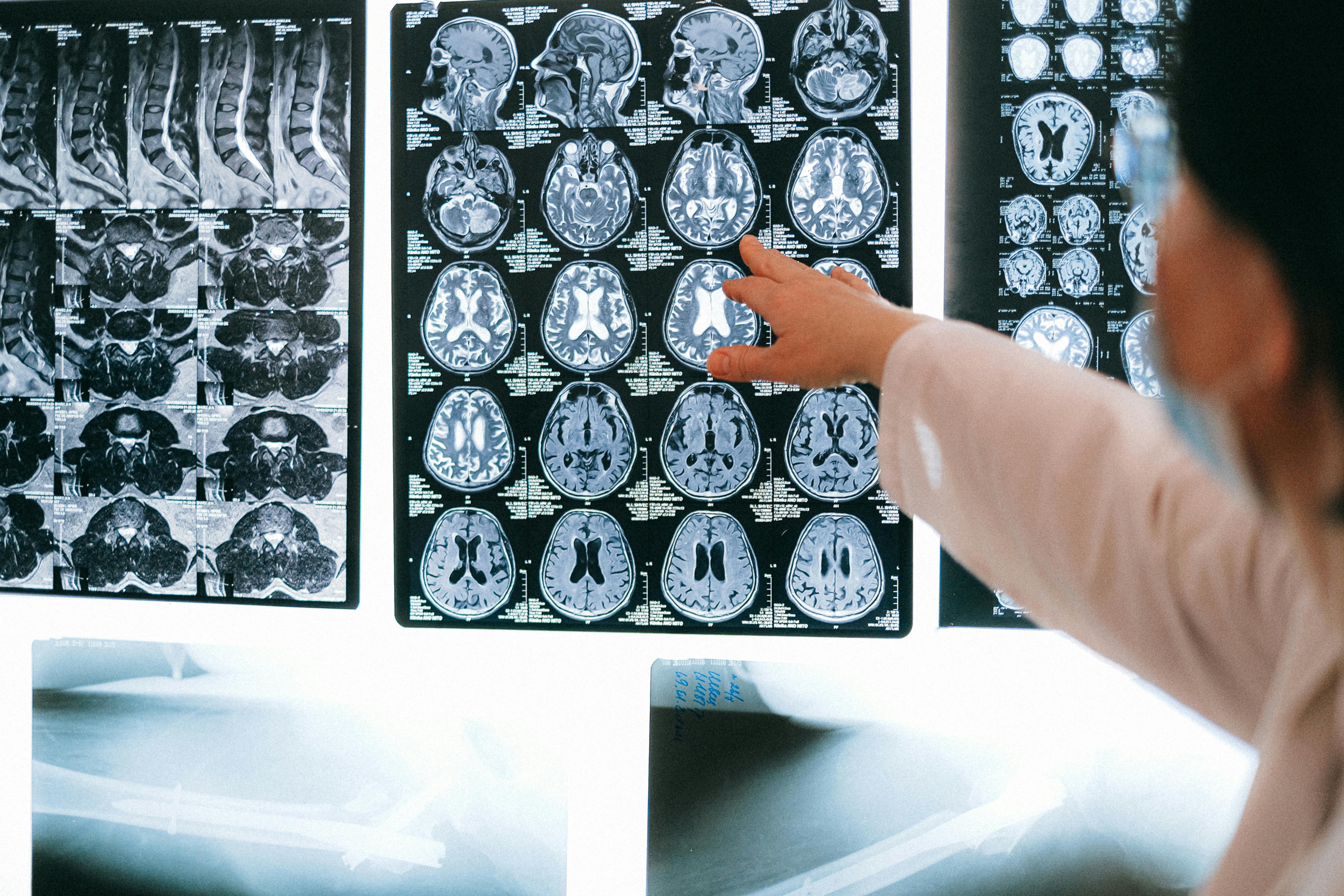
Biologic therapies aim to promote neuroregeneration, modulate neuroinflammation, and restore neural function in neurological disorders.
Common Conditions Treated
Stroke: Interruption of blood supply to the brain.
Traumatic Brain Injury: Damage to the brain from external force.
Spinal Cord Injury: Damage leading to loss of function.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
Multiple Sclerosis: Immune-mediated attack on the nervous system.
Treatment Modalities
Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapy: Uses high-quality MSCs to replace damaged neurons and support neurogenesis (formation of new neurons).
Exosome Therapy: Exosomes derived from MSCs deliver neuroprotective agents and modulate immune responses.
Procedure Overview
Patient Selection:
Inclusion Criteria: Patients with acute or chronic neurological deficits.
Exclusion Criteria: Active central nervous system infections or malignancies.
Preparation:
Informed Consent: Discuss the experimental nature, potential benefits, and risks.
Imaging: Obtain MRI or CT scans to identify target areas.
Administration:
Intranasal
Intravenous Infusion: Systemic delivery for widespread neuroprotection.
Post-Procedure Care:
Monitoring: Observe for neurological changes or adverse effects.
Rehabilitation: Implement physical and occupational therapy as needed.
Supporting Studies
Neural Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Neuroregeneration: This review explores the role of exosomes in neural repair and their therapeutic potential. Stem Cell Research
MSC-Derived Exosomes in Neurological Disorders: The study discusses the application of MSC-derived exosomes in treating neurological conditions.



About
Our mission is to equip practitioners with essential knowledge on biologics, covering protocols, regulatory guidelines, and foundational insights. This site serves as a trusted resource for navigating the evolving landscape of stem cell applications in clinical practice.
Disclaimer
The information on this website is provided solely for informational purposes and has not been reviewed or approved by the FDA or any other regulatory authority. It does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, treatment, or any guarantees of medical outcomes and should not be used as a substitute for formal medical education and training, nor as a substitute for consultation with qualified healthcare professionals. Similarly, the content does not provide legal advice or guidance on regulatory compliance and should not replace consultations with qualified legal professionals.
DiscoverBiologics.com makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, reliability, or applicability of the information provided to individual health circumstances or the legal use and adoption of biological products by clinics or providers.
By accessing this website, you agree to the terms and conditions outlined herein and accept full responsibility for compliance and clinical decisions made within your practice. You also acknowledge that you have been encouraged to review the disclaimer page and understand that any reliance on the information provided is voluntary and at your own risk and sole discretion.
2025 © All Rights Reserved. DiscoverBiologics.com
