Intravenous Therapy Treatment and Protocol
The purpose of this website is to provide educational information for practitioners on biologic materials, orthopedic protocols, regulatory considerations, and general best practices. This content is intended for professional education only and does not constitute medical advice or approved treatment recommendations.
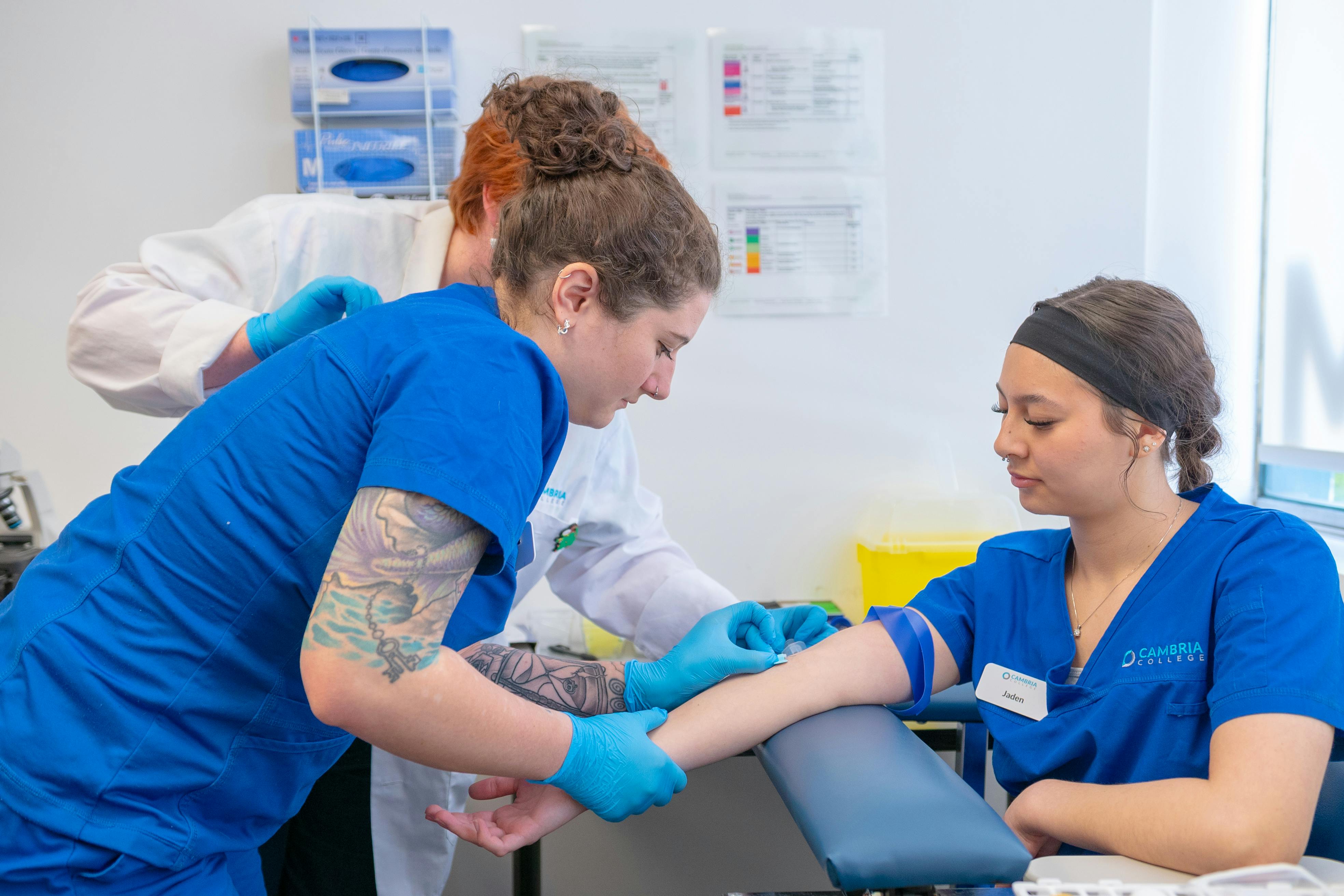
Introduction
Intravenous (IV) infusion of perinatal-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) represents a systemic delivery approach that leverages their paracrine, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory properties. Perinatal MSCs are considered immune-privileged due to their low expression of MHC-II and co-stimulatory molecules, making them suitable for allogeneic use. IV infusion distributes MSCs throughout the vascular system, where they interact with immune cells and release soluble bioactive factors, potentially benefiting systemic inflammatory, autoimmune, and degenerative conditions.
Indications and Viable Conditions
Perinatal stem cell IM therapy may be considered in patients with:
Chronic muscle injuries (hamstring, calf, rotator cuff, or quadriceps) not responding to conventional rehabilitation.
Myopathies of metabolic or inflammatory origin where adjunctive biologics may aid repair.
Peripheral artery disease–related ischemic myopathy (as studied in critical limb ischemia trials).
Postsurgical muscle loss or fibrosis (e.g., following orthopedic or tendon repair).
Adjunctive use in sports medicine for enhanced recovery in carefully selected athletes.
Greatest potential is in patients with persistent pain, weakness, or MRI-confirmed muscle pathology where conservative care has failed.
Patient Selection & Contraindications
Patient Selection
Ideal candidates include:
Adults with chronic inflammatory or autoimmune conditions not fully controlled by standard care.
Patients seeking adjunctive systemic modulation where biologics or immunosuppressants are limited or poorly tolerated.
Individuals with good cardiopulmonary reserve.
Contraindications
IV stem cell infusion should be avoided in:
Active systemic or localized infection.
Current or past malignancy within 5 years.
Severe heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, or unstable cardiovascular disease.
Severe immunosuppression or concurrent cytotoxic drug use.
Pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Dosing Considerations
Dosing is generally weight- and indication-dependent, with current clinical protocols utilizing:
Low dose: 20–40 million viable MSCs (immunomodulation, wellness applications).
Moderate dose: 50–100 million viable MSCs (autoimmune/inflammatory disease).
High dose: 150–200 million viable MSCs (systemic inflammatory/degenerative conditions, investigational use).
Infusions are delivered in 50–500 mL of normal saline over 20–60 minutes depending on dose. Dose ranges remain investigational; no FDA-approved standard exists.
Procedure Protocol (IV Infusion)
Pre-procedure preparation:
Obtain detailed medical history, informed consent, and baseline vitals.
Screen for contraindications (infection, malignancy, severe cardiac/pulmonary compromise).
Establish IV access (20–22G peripheral IV or central access if required).
Prepare perinatal MSC product under sterile conditions, suspended in normal saline.
Infusion procedure:
Verify product identity, cell count, and viability.
Connect infusion line with 0.22 µm filter to minimize risk of cell clumping.
Administer stem cell suspension in 50–500 mL normal saline.
Begin infusion slowly (first 10 minutes at 25–50 mL/hr).
If tolerated, increase rate to complete infusion within 20–60 minutes.
Monitor vital signs (BP, HR, O2 saturation) every 15 minutes during infusion.
Discontinue immediately if signs of hypersensitivity, chest pain, dyspnea, or hypotension occur.
Post-Procedure Protocol
Immediate monitoring: Observe patient for 60 minutes post-infusion for delayed reactions.
First 24–48 hours: Advise patient to avoid strenuous activity, alcohol, and NSAIDs that may blunt regenerative signaling.
Follow-up: Schedule clinical evaluation at 1 week, 1 month, and 3 months post-infusion.
Supportive measures: Encourage hydration, adequate rest, and adherence to baseline therapies.
Red flags: Instruct patients to report fever, persistent cough, chest pain, new rash, or neurologic symptoms.
Conclusion and References
Conclusion
Intravenous infusion of perinatal MSCs offers a systemic regenerative and immunomodulatory approach for patients with autoimmune, inflammatory, or degenerative disorders. Proper patient selection, careful dosing, and adherence to strict procedural protocols are essential to maximize benefit and reduce risk. This therapy remains investigational, and ongoing clinical trials will further define safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing regimens.
Conclusion
Shi Y, Wang Y, Li Q, Liu K, Hou J, Shao C, et al. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(8):493–507. doi:10.1038/s41581-018-0023-5
Leng Z, Zhu R, Hou W, Feng Y, Yang Y, Han Q, et al. Transplantation of ACE2– mesenchymal stem cells improves the outcome of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Aging Dis. 2020;11(2):216–28. doi:10.14336/AD.2020.0228
Squillaro T, Peluso G, Galderisi U. Clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells: An update. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(5):829–48. doi:10.3727/096368915X689622
Muroi K, Miyamura K, Ohashi K, Murata M, Eto T, Kobayashi N, et al. Bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase II study. Int J Hematol. 2016;103(2):243–50. doi:10.1007/s12185-015-1906-2
Ullah I, Subbarao RB, Rho GJ. Human mesenchymal stem cells—current trends and future prospective. Biosci Rep. 2015;35(2):e00191. doi:10.1042/BSR20150025
About
Our mission is to equip practitioners with essential knowledge on biologics, covering protocols, regulatory guidelines, and foundational insights. This site serves as a trusted resource for navigating the evolving landscape of stem cell applications in clinical practice.
Disclaimer
The information on this website is provided solely for informational purposes and has not been reviewed or approved by the FDA or any other regulatory authority. It does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, treatment, or any guarantees of medical outcomes and should not be used as a substitute for formal medical education and training, nor as a substitute for consultation with qualified healthcare professionals. Similarly, the content does not provide legal advice or guidance on regulatory compliance and should not replace consultations with qualified legal professionals.
DiscoverBiologics.com makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, reliability, or applicability of the information provided to individual health circumstances or the legal use and adoption of biological products by clinics or providers.
By accessing this website, you agree to the terms and conditions outlined herein and accept full responsibility for compliance and clinical decisions made within your practice. You also acknowledge that you have been encouraged to review the disclaimer page and understand that any reliance on the information provided is voluntary and at your own risk and sole discretion.
2025 © All Rights Reserved. DiscoverBiologics.com
